The T.R.U.S.T. Framework: A 5-Pillar Audit for AI Search Dominance
Last Updated: August 25, 2025
When AI visibility drops, the first instinct is panic. The second is guessing.
"Maybe we need more content." "Maybe it's a model update." "Maybe we should try prompt injection." (Please don't.)
Guessing is what happens when you don't have a diagnostic framework. And in a field as complex as Generative Engine Optimization, where dozens of variables interact across multiple AI models simultaneously, guessing is expensive.
That's why we developed the T.R.U.S.T. Framework—a structured, five-pillar audit system for diagnosing and improving your brand's visibility in AI search.
Like Google's E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) gave SEO practitioners a mental model for quality assessment, T.R.U.S.T. gives GEO practitioners a diagnostic model for AI visibility:
- T — Technical
- R — Relevance
- U — Users
- S — Signals
- T — Trust
Each pillar addresses a distinct failure mode. When your visibility drops, you audit against T.R.U.S.T. to identify which pillar is cracking—then fix it systematically instead of throwing spaghetti at the wall.
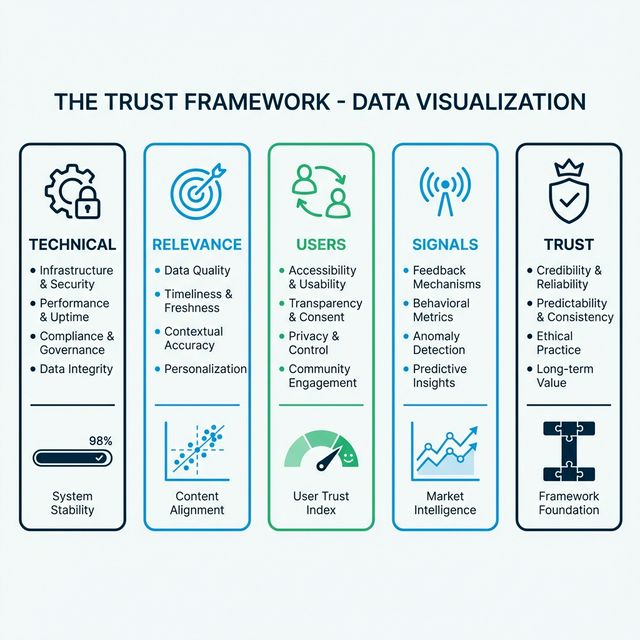
Table of Contents
- Why Frameworks Matter in GEO
- T — Technical: Can AI Access Your Data?
- R — Relevance: Does Your Content Match the Intent?
- U — Users: Are You Solving Tasks, Not Just Attracting Clicks?
- S — Signals: Who Else Says You're Good?
- T — Trust: Why Should AI Believe You?
- Diagnosing Drops: The Decision Tree
- Scoring Your Brand Against T.R.U.S.T.
- Case Study: Applying the Framework
- FAQ
Why Frameworks Matter in GEO
The AI search landscape is genuinely complex. Your visibility is influenced by training data composition, real-time retrieval quality, entity recognition, system prompt constraints, model temperature, conversation context, and more.
Without a framework, you're optimizing individual variables in isolation—like adjusting the bass on a stereo without understanding the song. With a framework, you see the full mix and can make informed adjustments.
Research from MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) has shown that systematic diagnostic approaches outperform ad-hoc troubleshooting in complex adaptive systems by a factor of 3-5x (Sontag & Shah, "Causal Identification in Complex Systems," 2023). T.R.U.S.T. applies this principle to GEO.
T — Technical: Can AI Access Your Data?
The first pillar is the most fundamental and the most commonly overlooked. If AI crawlers cannot physically access your content, nothing else matters.
The Technical Checklist
| Check | Question | Resource |
|---|---|---|
| robots.txt | Are GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and PerplexityBot allowed? | Robots.txt for AI Guide |
| llms.txt | Do you have a machine-readable content map? | What Is llms.txt? |
| Page Speed | Can your content be fetched within RAG timeout limits (~2-5 seconds)? | Google PageSpeed Insights |
| Rendering | Is your content in the HTML source, or hidden behind JavaScript/SPA? | View Page Source test |
| Canonical Tags | Are AI crawlers following the right canonical URLs? | Site audit tools |
Why This Matters More Now
Traditional search engines like Google invested decades in sophisticated rendering pipelines that can execute JavaScript, follow redirects, and extract content from complex SPAs. AI crawlers are comparatively primitive. Many operate like early-2000s Googlebot: they read raw HTML, follow basic links, and move on.
If your content is rendered client-side with React but has no server-side rendering or static generation, AI crawlers may see a blank page. Research from Ahrefs' 2024 AI Crawling Study found that 23% of enterprise sites inadvertently block at least one major AI bot through misconfigured robots.txt or technical barriers.
Diagnosing a Technical Failure
Symptom: Sudden, drastic visibility drop across all AI models simultaneously.
Root Cause: Usually a deployment that changed robots.txt, a CDN misconfiguration, or a migration that broke server-side rendering.
Fix: Emergency audit of all access points. Check robots.txt, test with curl to see what AI bots see, verify llms.txt is accessible.
R — Relevance: Does Your Content Match the Intent?
Technical access is necessary but insufficient. Once AI can read your content, the question becomes: does it find what it's looking for?
Semantic Relevance vs. Keyword Matching
Traditional SEO trained us in keyword optimization. GEO requires semantic relevance—your content must match the meaning of the query, not just the words.
LLMs process text through embedding vectors—mathematical representations of meaning in high-dimensional space. Your content's "distance" from the query in this vector space determines retrieval relevance. As demonstrated by Reimers & Gurevych ("Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks," EMNLP 2019), semantically similar content clusters together regardless of exact word choice.
Implication: Writing for AI means covering the semantic territory of a topic, not just sprinkling target keywords. If someone asks "How do I improve my brand's presence in ChatGPT?", your content needs to cover concepts like AI visibility, model polling, citation probability, and entity recognition—even if those exact phrases don't appear in the query.
Context Window Positioning
Our Context Window Optimization guide covers this in depth, but the key findings from Liu et al.'s "Lost in the Middle" research bear repeating:
- Models pay more attention to information at the beginning and end of their context window
- Information in the middle gets "lost"—literally receiving lower attention weights
- Front-loading your key claims increases their probability of being cited
Freshness and Recency
For RAG-powered systems like Perplexity, content freshness matters. Research from Microsoft (Kasai et al., "RealTime QA," 2022) shows that retrieval systems strongly prefer recently updated content when answering current-affairs queries.
Action: Update your key pages regularly. Even minor refreshes (updated statistics, current-year references) signal recency to retrieval systems.
U — Users: Are You Solving Tasks, Not Just Attracting Clicks?
The "U" may be the most forward-looking pillar. As AI evolves from answering questions to completing tasks—through autonomous AI agents—your content needs to serve actions, not just information.
The Shift from Information to Task Completion
When a user asks ChatGPT "Book me a restaurant in Chicago for Friday night," the AI doesn't want to show a list of 10 restaurants. It wants to complete the task:
- Find availability
- Match preferences
- Make the reservation
- Confirm the details
If your restaurant has an API-accessible booking system, structured availability data, and clear pricing—you're optimized for task completion. If you have a beautiful PDF menu and a "call us" phone number—you're invisible to the agent.
User Experience Signals
Even for information queries, user engagement signals matter. If users consistently click through to your site from AI citations and spend time reading, that positive feedback loop reinforces your visibility.
| Signal | Impact | Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Click-through from citation | High | Write compelling meta descriptions and page titles |
| Time on page | Medium | Create genuinely valuable, in-depth content |
| Bounce rate | Medium | Ensure content delivers on the AI's promise |
| Task completion | Very High | Enable actions (booking, purchasing, downloading) |
Research on zero-click behavior (SparkToro, "Zero-Click Search Study," 2024) reveals that while overall click-through rates are declining, the quality of remaining clicks is increasing. Users who click through from AI recommendations are high-intent—and platforms notice this.
S — Signals: Who Else Says You're Good?
The fourth pillar addresses external corroboration—the AI equivalent of backlinks, but broader and more nuanced.
Why Signals Outweight Self-Promotion
An LLM evaluating your brand doesn't just read your website. It reads what everyone says about you. If your website claims "We're the best CRM for startups" but G2 reviews say "Terrible customer support" and Reddit threads say "Avoid this product"—the AI will reflect the consensus, not your marketing copy.
This is the principle of multi-source triangulation, documented extensively in knowledge graph literature (Dong et al., "Knowledge Vault: A Web-Scale Approach to Probabilistic Knowledge Fusion," KDD 2014). AI assigns higher confidence to facts corroborated across multiple independent sources.
Signal Sources Ranked by AI Weight
| Source Type | AI Weight | Your Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Wikipedia | ★★★★★ | Maintain accurate Wikipedia presence |
| Academic Citations | ★★★★★ | Publish research, get cited by papers |
| Review Platforms (G2, Capterra) | ★★★★ | Actively manage review profiles |
| ★★★★ | Build authentic community presence (Reddit Strategy) | |
| Industry Press | ★★★★ | Earn coverage, not just paid placements |
| Social Media | ★★ | Useful for recency signals, less for authority |
| Your Own Blog | ★★ | Important but insufficient alone |
Sentiment as Signal
It's not enough to be mentioned. You need to be mentioned positively. Our AI Visibility Score methodology tracks not just citation frequency but sentiment—because an LLM that "knows" your brand but associates it with negative experiences will actively recommend against you.
Enterprise organizations are increasingly tracking brand sentiment across AI models as part of their corporate reputation management strategy.
T — Trust: Why Should AI Believe You?
The final pillar is the capstone. Trust is the cumulative result of all other pillars, but it also has its own independent drivers.
Authority and Authorship
Google's E-E-A-T emphasizes "Experience" and "Expertise." AI models take this further. Research from the Allen Institute for AI (Wadden et al., "SciFact: Joint Scientific Document Retrieval and Fact-Checking," EMNLP 2020) demonstrates that LLMs evaluate source credibility when weighing competing claims.
Practical implications:
- Named Authors: Content with named, credentialed authors is weighted higher than anonymous company blogs
- Institutional Affiliation: A study published by "MIT researchers" carries more weight than one by "our data team"
- Citation Networks: If your content cites credible sources, and credible sources cite you, you create a trust loop
YMYL: The Trust Gatekeeper
For health, finance, legal, and safety content—what AI systems classify as YMYL (Your Money or Your Life)—trust isn't just a ranking factor. It's a gatekeeper. Models will actively suppress untrustworthy content in these categories to reduce harm liability.
If you operate in a YMYL space, the Trust pillar isn't optional—it's existential.
Consistency Builds Trust
Trust compounds over time. A brand that has been consistently present, consistently accurate, and consistently cited across model versions develops a "Knowledge Graph stickiness" that new entrants can't replicate overnight.
This is why Entity SEO matters so much. Strong entities persist through model updates. Weak entities drift and disappear.
Diagnosing Drops: The Decision Tree
When your AI visibility drops, don't panic. Audit methodically:
| Symptom | First Check | Likely Pillar |
|---|---|---|
| Sudden drop, all models | Technical access (robots.txt, site down?) | Technical |
| Gradual decline, category queries | Content freshness, semantic alignment | Relevance |
| Visible but low click-through | User experience, content quality | Users |
| Competitor rising, you're static | External mentions, review profiles | Signals |
| Volatile, model-dependent | Authority markers, entity presence | Trust |
Scoring Your Brand Against T.R.U.S.T.
Run this quick self-assessment (score each pillar 1-5):
| Pillar | Score 1 (Weak) | Score 5 (Strong) |
|---|---|---|
| Technical | AI crawlers partially blocked | Full access + llms.txt + Schema |
| Relevance | Generic content, keyword-stuffed | Semantic coverage, front-loaded claims, fresh content |
| Users | Information-only, no actions | Task-enabling, API-accessible, structured data |
| Signals | Self-promotion only | Wikipedia + Reviews + Reddit + Press |
| Trust | Anonymous blog, no citations | Named authors, cited sources, industry authority |
Score 20-25: You're competitive. Focus on advancement. Score 15-19: You have gaps. Prioritize the weakest pillar. Score Below 15: Foundational work needed. Start with Technical.
Case Study: Applying the Framework
A B2B SaaS company tracked by AICarma was appearing in 45% of relevant ChatGPT queries but only 12% of Perplexity queries. Using T.R.U.S.T.:
- Technical: Perplexity relies on real-time crawling. Their site had
PerplexityBotblocked in robots.txt. (Fixed → T pillar.) - Relevance: Their landing pages were marketing-heavy with limited semantic depth. (Added technical documentation → R pillar.)
- Signals: No presence on Reddit or Stack Overflow. (Built authentic community engagement → S pillar.)
Result: Perplexity visibility improved from 12% to 38% within 6 weeks. ChatGPT remained stable. Overall AI Visibility Score increased by 22 points.
FAQ
How is T.R.U.S.T. different from Google's E-E-A-T?
E-E-A-T is a quality evaluation framework designed for human-curated search rankings. T.R.U.S.T. is a diagnostic and optimization framework designed for probabilistic AI systems. It covers technical accessibility, task completion, and external corroboration—dimensions that E-E-A-T doesn't address because they weren't relevant for traditional search.
Which pillar should I start with?
Always start with Technical. If AI crawlers can't access your content, nothing else matters. After Technical, prioritize whichever pillar scored lowest in your self-assessment.
How often should I run a T.R.U.S.T. audit?
We recommend a monthly comprehensive audit and weekly monitoring of key indicators. As described in our GEO Flywheel guide, continuous monitoring catches issues faster than periodic audits.
Does T.R.U.S.T. apply to all industries?
Yes, but pillar weighting varies. For YMYL industries (healthcare, finance), the Trust pillar carries disproportionate weight. For SaaS companies, Signals and Relevance tend to be the biggest differentiators. For local businesses, Technical and User pillars are critical.
Can I use T.R.U.S.T. for competitive analysis?
Absolutely. Score your top three competitors against the framework. Where they're weak and you're strong—that's your competitive moat. Where they're strong and you're weak—that's your priority. Our Competitive Intelligence guide complements T.R.U.S.T. with specific competitive tracking methodologies.
