Corporate Reputation in the AI Age: From Search Rankings to Share of Model
Last Updated: December 5, 2025
When consumers ask ChatGPT "What's the safest family SUV?", they're no longer visiting ten websites to form an opinion. They're trusting the AI to synthesize that opinion for them—in a single, authoritative-sounding paragraph.
For enterprise brands, this represents a fundamental shift in how reputation forms. Your carefully optimized Google rankings matter less if the AI doesn't mention you. Your press releases don't help if the model doesn't include you in recommendations.
Welcome to the era of Share of Model—and the companies that understand it are rewriting the rules of corporate reputation management.
Table of Contents
- The Reputation Paradigm Shift
- From SEO to GEO: New Rules for Visibility
- Understanding Share of Model
- The Hallucination Risk: When AI Gets You Wrong
- Real-Time Reputation Monitoring
- Enterprise AI Reputation Strategy
- FAQ
The Reputation Paradigm Shift
For two decades, corporate reputation online meant winning search results. SEO teams optimized content, PR teams earned coverage, and success meant appearing in the top 10 blue links when customers searched your category.
That model is fracturing.
The Zero-Click Reality
By 2026, analysts project that 30-50% of product research will happen through AI assistants rather than traditional search. Users increasingly trust ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity to synthesize answers—and never click through to underlying sources.
This is zero-click search taken to its logical extreme. The AI doesn't send traffic—it provides answers directly.
What This Means for Enterprise Brands
Consider the implications:
- Your visibility becomes the AI's mention, not the search ranking
- Sentiment isn't what journalists write—it's what models say
- Authority isn't measured by backlinks—it's measured by citations in AI responses
The enterprise companies ahead of this curve aren't just monitoring search rankings anymore. They're monitoring what AI models say about them—across every model, every prompt type, every competitive context.
From SEO to GEO: New Rules for Visibility
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) represents the strategic response to this shift. Where SEO optimized for search engine algorithms, GEO optimizes for Large Language Model outputs.
Key Differences
| Dimension | Traditional SEO | Generative Engine Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Rank in search results | Be cited in AI responses |
| Success metric | Position, traffic | Mention rate, sentiment, citation authority |
| Optimization target | Search algorithms | LLM training data and RAG sources |
| Content approach | Keywords, links | Entity clarity, structured data, authoritative content |
| Timeline | Days to see changes | Months (training data) or real-time (RAG) |
The Entity Imperative
AI models "understand" the world through entities—people, companies, products, concepts. If your brand lacks clear entity representation in the model's training data, you may not exist to the AI at all.
Building entity presence requires:
- Consistent, well-structured content across authoritative sources
- Proper schema markup that clarifies what your brand is
- Citation in sources that AI models treat as authoritative (Wikipedia, major publications, industry databases)
- Clear differentiation from competitors and similar-named entities
Understanding Share of Model
Share of Model applies the classic "Share of Voice" concept to AI outputs. Where Share of Voice measured how often you were mentioned across media, Share of Model measures how often you appear in AI-generated responses.
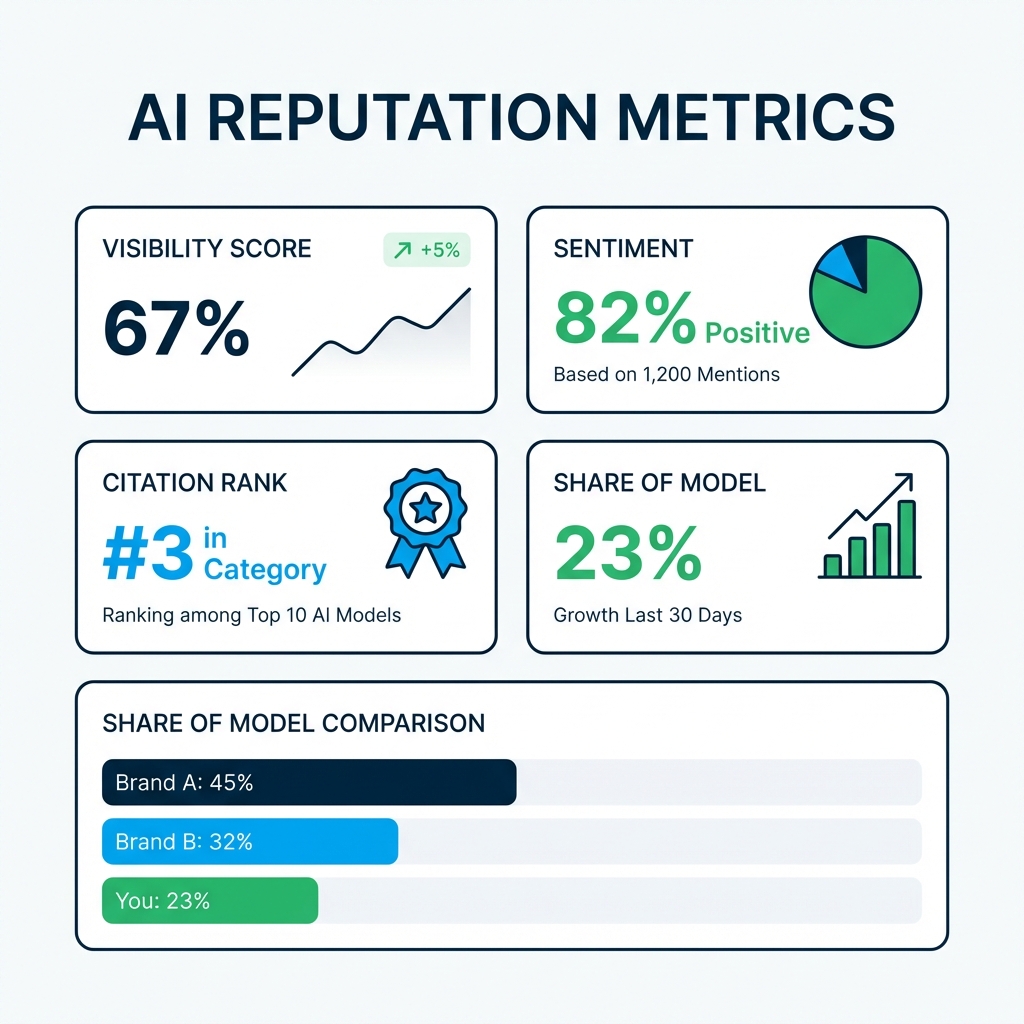
The Core Metrics
Visibility Score: What percentage of relevant prompts result in your brand being mentioned?
Sentiment Analysis: When mentioned, is the context positive, neutral, or negative?
Citation Rank: Where do you appear in lists? First recommendation vs. mentioned fifth?
Share of Model: What percentage of category mentions belong to you vs. competitors?
Cross-Model Variance
One of the most surprising discoveries for enterprise teams: different AI models have radically different "opinions" about the same brands.
A brand might have 65% visibility in ChatGPT but only 20% in Claude—due to different training data, different retrieval sources, and different model "personalities."
This is why multi-model monitoring is essential. Optimizing for one model while invisible in others leaves significant blind spots.
The Hallucination Risk: When AI Gets You Wrong
AI models don't just fail to mention brands—they sometimes mention them incorrectly. The phenomenon of hallucination represents an existential risk for enterprise reputation.
The Air Canada Precedent
A landmark case established the stakes. Air Canada's customer service chatbot, powered by AI, promised a customer a bereavement discount that didn't exist in company policy. When the customer requested the promised discount, Air Canada argued the chatbot was a "separate legal entity" not bound by the company.
The court disagreed. Air Canada was held fully liable for its AI's statements.
This precedent transformed AI monitoring from a marketing concern to a legal necessity. If an AI—your own or a third-party model—makes false claims about your products, services, or policies, the reputational and legal consequences are real.
Monitoring for Accuracy
Enterprise reputation monitoring must now include:
- Tracking what AI models say about your products
- Identifying factual errors before they spread
- Detecting negative sentiment drift
- Flagging potential hallucinations about policies, capabilities, or claims
Research shows hallucination rates vary dramatically by model—from under 5% in controlled contexts to over 30% in open-ended generation. Continuous monitoring catches problems before they compound.
Real-Time Reputation Monitoring
Traditional brand monitoring measured media coverage, social mentions, and survey responses. AI reputation monitoring operates on different axes.
What to Monitor
Model Responses: What do GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, and Perplexity say when asked about your brand, category, or key topics?
Competitive Positioning: How do you compare to competitors in AI recommendations?
Sentiment Trends: Is the model's "opinion" of your brand improving or degrading over time?
Factual Accuracy: Are statements about your brand, products, and policies correct?
Source Attribution: When AI cites sources about your brand, which sources appear? Are they favorable?
The Real-Time Imperative
AI models that incorporate real-time retrieval (RAG) can shift their responses within hours as new information enters their context windows. A crisis that surfaces on Reddit today can appear in ChatGPT responses tomorrow.
This is why real-time monitoring matters. Monthly brand tracking reports no longer capture the speed at which AI-mediated perception changes.
Enterprise Monitoring Platforms
Purpose-built platforms like AICarma address this need by:
- Polling 10+ AI models simultaneously on relevant prompts
- Tracking visibility, sentiment, and ranking over time
- Alerting on significant changes or accuracy issues
- Providing competitive benchmarking across models
What once required manual polling across multiple interfaces now operates as continuous, automated surveillance—essential infrastructure for enterprise reputation management.
Enterprise AI Reputation Strategy
Managing reputation in the AI age requires updated playbooks.
Immediate Actions
-
Audit Current State: Query major AI models about your brand, products, and category. Document what they say. Note inaccuracies.
-
Implement Monitoring: Deploy continuous AI monitoring to track changes across models and time.
-
Review Technical Foundation: Ensure your website and content are properly structured for AI discovery—robots.txt, schema markup, llms.txt.
Medium-Term Strategy
-
Entity Building: Strengthen your brand's entity presence in sources that influence AI training—Wikipedia, Wikidata, Crunchbase, authoritative industry databases.
-
Content Strategy Shift: Develop content optimized for AI citation—clear, authoritative, well-sourced material that AI wants to reference.
-
Competitive Intelligence: Monitor competitor visibility and sentiment to identify positioning opportunities.
Long-Term Investment
-
Stakeholder Education: Train marketing, PR, legal, and executive teams on AI reputation dynamics.
-
Integration with Existing Platforms: Connect AI reputation data with broader corporate intelligence systems.
-
Continuous Iteration: As AI models evolve, reputation strategies must evolve with them.
FAQ
How is Share of Model different from Share of Voice?
Share of Voice measures presence across media channels—press mentions, social posts, advertising impressions. Share of Model specifically measures how often AI models cite or recommend your brand when answering relevant queries. A brand can have high Share of Voice and low Share of Model if AI models don't reflect their media presence.
Can we influence what AI models say about us?
Yes, but not through traditional advertising. AI models are influenced by training data (content that existed when the model was trained), retrieval sources (content accessed in real-time via RAG), and entity relationships in knowledge graphs. Strategies include improving authoritative content, ensuring accurate information across key sources, and building entity presence.
What happens if an AI model makes false statements about our company?
Legal precedent (Air Canada case) suggests companies can be held liable for their own AI's statements. For third-party models making false statements, remedies are still evolving—but typically involve correcting inaccurate source material and, in some cases, direct engagement with AI platform providers.
How quickly do AI reputations change?
It depends on the model architecture. Base model "opinions" change slowly—only when models are retrained or fine-tuned. But models using RAG (real-time retrieval) can shift within hours as new information becomes available. This is why real-time monitoring is essential.
Is AI reputation monitoring relevant for B2B companies?
Absolutely. Enterprise buyers increasingly use AI assistants for vendor research, comparison, and recommendation. A B2B brand that appears negatively or not at all in AI responses to buyer queries faces the same visibility challenges as consumer brands.
What's the relationship between GEO and traditional SEO?
GEO and SEO are complementary. Many GEO best practices (structured content, authoritative sources, clear entity representation) also improve SEO. But they require different prioritization and different success metrics. Enterprise teams increasingly run parallel SEO and GEO programs.
The companies that master AI reputation management today are building competitive moats for the next decade. As more consumers and enterprise buyers trust AI recommendations over search results, Share of Model will become as important as market share itself. The question isn't whether your brand will be evaluated by AI—it's whether you'll be monitoring, optimizing, and managing that evaluation, or leaving it to chance.
